Table of Contents
The Maurya Empire: A Brief History
The Maurya Empire, which existed from the 4th century BCE to the 2nd century BCE, was one of the most powerful and influential empires in the ancient Indian subcontinent. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya, the empire spanned a vast territory, encompassing the Indian subcontinent and parts of present-day Afghanistan and Iran. Under the rule of Chandragupta and his successors, notably Ashoka the Great, the Maurya Empire witnessed significant political, military, and cultural achievements.
The Founding of the Maurya Empire
The foundation of the Maurya Empire marked a turning point in the ancient history of the Indian subcontinent. In the 4th century BCE, Chandragupta Maurya, the founder of the empire, overthrew the Nanda dynasty, which had ruled the region. With the establishment of the Maurya Empire, Chandragupta laid the foundation of what would become one of the greatest empires in ancient India.
Chandragupta Maurya: The Founder

Chandragupta Maurya, the founder of the Maurya Empire, was an ambitious ruler who led conquests that established the empire’s vast territorial extent. He was the first Mauryan king, known for his political and military acumen. Under his rule, the Mauryan Empire expanded its influence across the Indian subcontinent, becoming the dominant power in the region. Chandragupta Maurya’s reign marked the beginning of the dynasty’s power, which lasted for several generations and left a lasting impact on the history of ancient India.
Role of Chanakya in Establishing the Empire
One of the key figures in the establishment of the Maurya Empire was Chanakya, who served as the prime minister of the empire. Also known as Kautilya or Vishnugupta, Chanakya played a crucial role in the political success of Chandragupta Maurya and later, his grandson Ashoka. He was a strategist, economist, and political advisor, who played a pivotal role in the centralization and governance of the empire. Chanakya’s policies and economic system, known as the “Arthashastra,” contributed to the empire’s growth and stability.
Under the guidance of Chanakya, the Mauryan Empire flourished, with central India serving as the epicentre of power. The council of ministers, led by the prime minister, played an active role in the empire’s governance, ensuring effective administration and efficient decision-making. The chief minister, appointed by the king, had a significant influence on the day-to-day affairs of the empire, and the council of ministers worked in tandem to implement policies, maintain law and order, and regulate the administrative machinery of the empire.
Conquests and Expansion under the Maurya Rule
The Mauryan Empire, known for its military prowess, witnessed extensive conquests and territorial expansion during its reign. Under the rule of Chandragupta Maurya and his successors, the empire expanded its dominion across the vast expanse of the Indian subcontinent, including the Punjab region and northern India. Through successful conquests and military campaigns, the Mauryan Empire established its authority over regions that were previously under the control of the Nanda dynasty and other regional powers.
The Conquest of the Nanda Empire
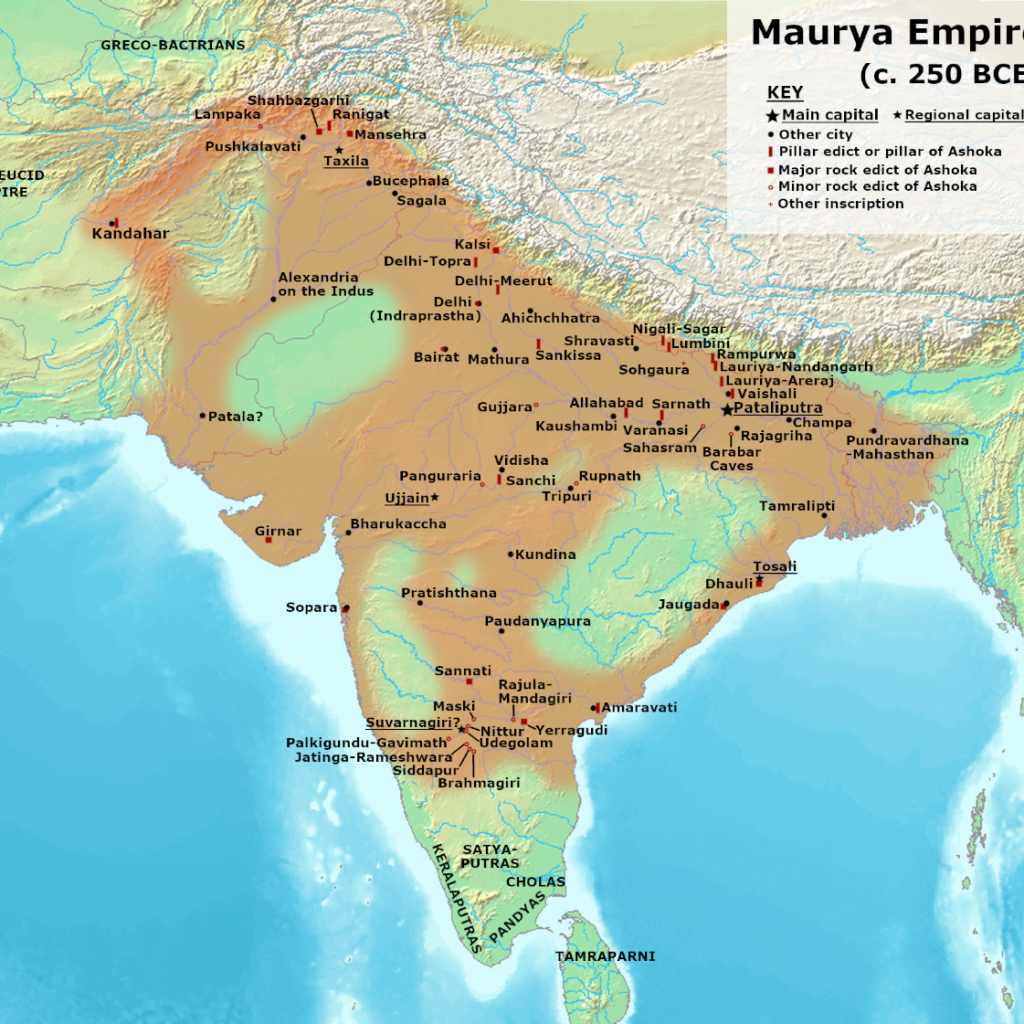
One of the Mauryan Empire’s significant conquests was overthrowing the Nanda dynasty, which ruled over parts of northern India. Under the leadership of Chandragupta Maurya, the small armies of the Mauryan Empire strategically seized the territories of the Nanda dynasty, marking the beginning of the empire’s expansion. The Maurya dynasty’s advanced history of war elephants played a crucial role in the conquest, allowing them to overcome the Nanda dynasty’s defences.
North-west Expansion and Alliance with Seleucus
Another significant aspect of the Mauryan Empire’s expansion was the northwest region, which included parts of present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan. Under the reign of Chandragupta Maurya, the empire expanded its influence beyond the Indus River, reaching areas near the Hindu Kush mountains. The Mauryan Empire established friendly relations with the Seleucid Empire, a Hellenistic state that controlled parts of western India. This alliance with the Seleucid Empire further strengthened the Mauryan Empire’s regional power, opening doors for trade and cultural exchange.
Reign of Ashoka the Great
After the rule of Chandragupta Maurya, the empire passed into the hands of his son, Bindusara, and later, his grandson, Ashoka the Great. Ashoka, who is often regarded as one of ancient India’s greatest emperors, ascended the throne in the 3rd century BCE. Ashoka’s reign marked the pinnacle of the Mauryan Empire’s power, with the empire attaining its greatest extent under his rule. As an Indian emperor, Ashoka’s vast empire covered large parts of the Indian subcontinent and extended its influence beyond its borders.
Ashoka’s Conquest of Kalinga
One of the most significant events during Ashoka’s reign was his conquest of Kalinga, a region located on the eastern coast of ancient India. The war against Kalinga was a turning point in Ashoka’s life and the history of the Mauryan Empire. The fierce battle witnessed bloodshed on a massive scale, leaving a deep impact on Ashoka’s conscience. Moved by the horrors of war, Ashoka renounced violence and embraced Buddhism, marking a significant shift in the empire’s religious policies.
Transformation to Buddhism: A Turning Point
The transformation of Emperor Ashoka to Buddhism was a transformative moment not only in his life but also in the history of the Mauryan Empire. After witnessing the devastation caused by the war with Kalinga, Ashoka turned to Buddhism, finding solace in its teachings of compassion and non-violence. Hailed as a great patron of Buddhism, Ashoka actively propagated the faith, erecting pillars inscribed with edicts that promoted ethical conduct, social welfare, and the spread of Buddhist principles. Influenced by Buddhist texts and sources, the empire underwent a profound transformation, emphasizing the common economic system, civil service, and administration for the betterment of society.
Military and Administration under the Maurya Empire
The Mauryan Empire was known for its well-organized military and effective administrative system. The empire maintained a standing army, comprising infantry, cavalry, and war elephants, which played a crucial role in the empire’s defense and conquests. The Mauryan kings, with the help of their council of ministers, spearheaded the centralization of power, ensuring the empire’s governance and the loyalty of regional governors. The empire also implemented a taxation system, primarily based on land revenue, which provided the necessary resources for the empire’s functioning and the maintenance of the armed forces.
Unification and Military Strategies

One of the remarkable achievements of the Mauryan Empire was the unification of the Indian subcontinent. The Mauryan kings, with their standing army and military strategies, successfully expanded the empire’s territory, subduing regional kings and incorporating their realms into the central authority. The Mauryan dynasty’s advanced history of war elephants played a vital role in the empire’s military campaigns, making them a formidable force on the battlefield. The centralization of power, backed by the standing army, played a significant role in maintaining political unity, as well as effectively quelling any dissent or rebellion within the empire.
Centralization and Taxation System

Centralization and an efficient taxation system were key pillars of the Mauryan Empire’s administration. The empire’s centralization of power allowed for effective governance, with the Mauryan court serving as the seat of political authority. The council of ministers, led by the chief minister, played a pivotal role in the empire’s administration, ensuring the smooth functioning of the empire’s machinery. The taxation system, primarily based on land revenue, provided the necessary funds for the empire’s activities, including the maintenance of the standing army, public works, and the welfare of the empire’s subjects.
Culture, Religion and Society in the Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, an ancient Indian empire founded by Chandragupta Maurya, had a geographically extensive Iron Age presence. The empire, under the rule of King Ashoka, saw a remarkable transformation due to his conversion to Buddhism and subsequent propagation of the faith. This pivotal move influenced the culture, religion, and society of the empire, making Buddhism a prominent feature of Mauryan life. King Bindusara’s son, Ashoka, established himself as a legendary Indian emperor, extending the boundaries of the Maurya Empire across the Indian subcontinent in the 2nd century BCE. This expansion led to a fusion of various cultural and religious practices, shaping the identity of the Maurya Empire.
Influence of Buddhism on Society
The influence of Buddhism on society during the Maurya Empire was profound and far-reaching. King Ashoka’s active promotion of Buddhism played a pivotal role in shaping societal norms. This was evident in the emperor’s edicts, inscribed on pillars, which reflected the widespread influence of Buddhism on various aspects of society. Furthermore, Buddhist sources emphasized the correlation between Ashoka’s policies and the overall welfare of the society, highlighting the interconnectedness between governance and societal well-being.
Architectural remains from the Maurya Empire era also depicted the significant impact of Buddhism, particularly through the construction of stupas. These structures not only served as religious monuments but also symbolized the cultural and societal significance of Buddhism during that time. The active loyalty of the Indian emperor towards Buddhism further influenced the empire’s cultural and societal norms, creating a lasting legacy that shaped ancient India in the 2nd century BCE.
Cultural Exchange during Ashoka’s Rule
Ashoka’s rule marked a period of extensive cultural exchange with the western border regions, fostering diplomatic relations with the Seleucid empire. The historical ties with Sri Lanka also contributed to cultural diffusion during the Mauryan period. Notably, the empire’s golden age witnessed significant advancements in art, architecture, and language, reflecting the depth of cultural exchange. Additionally, friendly relations with the Greek ambassador, Megasthenes, played a pivotal role in facilitating and enhancing these exchanges. This cultural efflorescence during Ashoka’s reign underscored the Mauryan empire’s influence as an Indian emperor and its impact on ancient India, further solidifying its significance as a geographically extensive Iron Age Indian empire in the 2nd century BCE.
Architecture and Arts in the Mauryan Period
The Mauryan period in ancient India witnessed remarkable architectural and artistic achievements, leaving behind a rich historical legacy. The empire’s architectural marvels, such as the Sanchi Stupa, continue to hold immense religious significance. Stone carvings depicting Mauryan art are a testament to the empire’s cultural and artistic prowess.

The extensive geographical reach of the empire, spanning across the Gangetic plain and northern India, reflects its architectural and artistic influence. Moreover, during the reign of King Ashoka, armed cities were constructed, and Buddhism was widely propagated through art, further showcasing the empire’s impressive cultural and artistic contributions to Indian history.
Architectural Remains and Their Significance
The architectural remains of the Mauryan Empire hold immense historical significance, particularly the iconic Sarnath pillar. These stone pillars, bearing inscriptions of edicts, serve as a reflection of the policies and beliefs held by the Mauryan kings. Ambassadors, such as Megasthenes, provided detailed accounts of the advanced history of the Mauryan Empire, offering valuable insights into its architectural prowess.

The extensive Iron Age architecture of the Mauryan dynasty symbolizes the empire’s grandeur and power, showcasing its significance in ancient India. Notably, the foundation of the Shunga dynasty by Bindusara’s son, King Ashoka, played a crucial role in influencing the preservation of these historical sites, marking a pivotal era in Indian history. The architectural legacy of the Mauryan Empire endures as a testament to its remarkable contributions to the rich tapestry of Indian heritage.
The Decline of the Maurya Empire
As the Maurya Empire reached its peak, internal strife and external invasions played a significant role in its decline. The empire became vulnerable due to weak successors, leading to regional governors gaining independence. Simultaneously, the invasion of Central Asian tribes further weakened the empire’s foothold, ultimately resulting in its disintegration. King Ashoka’s propagation of Buddhism, although impactful, diverted attention and resources from the administration, contributing to the decline. The once geographically extensive Iron Age Indian Empire started to fragment and dissolve by the mid-2nd century BCE, marking the end of an era in ancient India.
Internal Strife and the Sunga Coup

Amidst the Mauryan dynasty’s council of ministers, internal strife emerged, eroding the empire’s unity. This power struggle culminated in the establishment of the Shunga dynasty by Pushyamitra Shunga, signalling the end of the Mauryan reign. The court’s relentless pursuit of power and influence fueled instability, hastening the empire’s decline and paving the way for the rise of the Shunga dynasty in eastern India. The assassination of the Mauryan king and the subsequent ascension of the Shunga dynasty epitomized the political turmoil that engulfed the once-mighty empire. This period of transition and conflict reshaped the ancient Indian empire, marking a significant shift in the geographically extensive Iron Age Indian empire in the 2nd century BCE.
Impact of the Indo-Greek Kingdom
The decline of the ancient Indian empire, in the 2nd century BCE, created an opportunity for the geographically extensive Iron Age Indo-Greek kingdom to expand its influence in northwestern India. This expansion was triggered by the loss of western India by the founder of the Maurya Empire, which ultimately led to the establishment of the Indo-Greek kingdom in the region. The reign of the Indo-Greek king in the former territories of the Indian empire marked the end of the Mauryan dynasty’s influence, as the Indo-Greek kingdom gained control over the Punjab region. Consequently, the Indo-Greek kingdom was able to establish its rule in the Indus River region, solidifying its position and significance in ancient India.
Who were the Mauryas and what were their major achievements?
The Mauryas were a dynasty that ruled over the Indian subcontinent from 322 to 185 BCE. Their major achievements include the unification of most of India, the establishment of a strong centralized government, and the promotion of Buddhism under Emperor Ashoka.
How did the Maurya Empire Influence Indian Civilization?
The Maurya Empire played a crucial role in shaping the Indian subcontinent through its political unity. Under the reign of King Ashoka, the empire reached its greatest extent. The Mauryan edicts and public works stand as powerful indicators of its historical influence. Ancient texts also highlight its vast territory and friendly relations with foreign powers. The empire’s civil service and common economic system further solidified its extensive reach.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Maurya Empire was a significant period in Indian history that left a lasting impact on its civilization. From its humble beginnings under Chandragupta Maurya and the strategic guidance of Chanakya to the vast conquests and expansion under Ashoka the Great, the empire showcased remarkable military prowess and administrative skills. The empire’s embrace of Buddhism brought about a cultural and societal transformation, promoting peace and tolerance.
The architectural remains of the Mauryan period stand as a testament to their grandeur and artistic achievements. However, internal strife and the influence of the Indo-Greek Kingdom eventually led to the decline of the empire. To explore further, redirect to our blog on the Chanakya, Secret Society etc.
FAQS
1. When did the Maurya Empire start and end?
The Maurya Empire began in the 4th century BCE when Chandragupta Maurya overthrew the Nanda dynasty and ended in the 2nd century BCE when the empire declined due to internal strife and the rise of the Indo-Greek Kingdom.
2. Why is the Maurya Empire famous?
The Maurya Empire is famous for its political unity, military prowess, and cultural achievements. It was one of the most powerful and influential empires in the ancient Indian subcontinent, and its policies and edicts have left a lasting impact on Indian civilization.
3. Is the Maurya Empire a dynasty or an empire?
The Maurya Empire was both a dynasty and an empire. It was a dynasty because it had a hereditary line of rulers, and it was an empire because it expanded vastly and ruled over a large territory, influencing various aspects of society.
4. What were the major achievements of the Maurya Empire?
The major achievements of the Maurya Empire include the unification of most of India, the establishment of a strong centralized government, and the promotion of Buddhism under Emperor Ashoka.
5. How did the Maurya Empire influence Indian Civilization?
The Maurya Empire influenced Indian civilization by bringing about political unity, extensive territorial expansion, and cultural transformation. The empire’s policies and public works, such as the Mauryan edicts, left a lasting impact on Indian civilization.
6. What was the role of Chanakya in the Maurya Empire?
Chanakya, also known as Kautilya or Vishnugupta, served as the prime minister of the Maurya Empire and played a crucial role in its political success. He was a strategist, economist, and political advisor, and his policies and economic system, known as the “Arthashastra,” contributed to the empire’s growth and stability.
7. What were the architectural and artistic achievements of the Maurya Empire?
The Maurya Empire witnessed remarkable architectural and artistic achievements, such as the construction of the Sanchi Stupa, stone carvings depicting Mauryan art, and the construction of armed cities during King Ashoka’s reign.






